Purchase IoTKit
Please refer to TQLOne for options to purchase your copy of IoTKit
Meet Your IoTKit
List of things that are contained in the IoTKit
Name | Image | Description |
Raspberry Pi 3 Model 3 | | The Raspberry Pi 3 is the third generation Raspberry Pi. It replaced the Raspberry Pi 2 Model B in February 2016. Compared to the Raspberry Pi 2 it has: - A 1.2GHz 64-bit quad-core ARMv8 CPU
- 802.11n Wireless LAN
- Bluetooth 4.1
- Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE)
Default login password for Raspberry pi are: pi / raspberry |
Arduino Uno and Arduino Sensor Shield | | The Uno is a microcontroller board based on the ATmega328P. It has 14 digital input/output pins (of which 6 can be used as PWM outputs), 6 analog inputs, a 16 MHz quartz crystal, a USB connection, a power jack, an ICSP header and a reset button. |
Sensors | | - Ambience Light Sensor
- Thermistor
- DHT11 sensor
|
USB camera | | The USB camera is easy to use and it is interfaced to Pi. |
Micro Servo motor | | The micro servo motor can rotate at angle between 0 and 180 degrees and it is to be interfaces to the Arduino. |
| RGB 3-Color LED Module | | This LED light can be set in one of the three colors – Red, Green or Blue. Provided 3 lights. |


The following steps will setup the Wireless connection on raspberry pi.
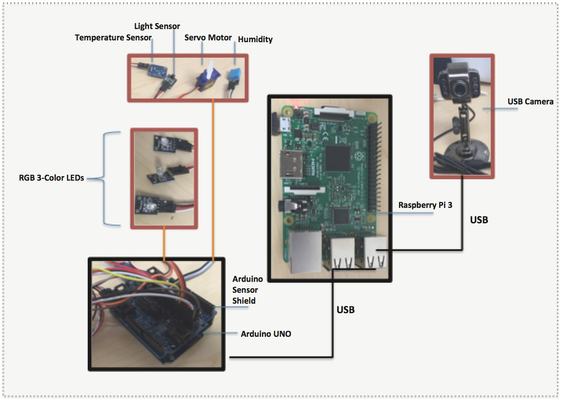
- Connect USB cable (A in Figure above) from Arduino to Raspberry Pi USB Port (Any of the four available)
- Connect USB cable (B in Figure above) from USB Camera to Raspberry Pi USB Port (Any of the four available)
- Connect mini USB power cable (C in Figure above) to Raspberry Pi mini USB power port and power supply.
- Wait for Raspberry Pi to startup.
- Raspberry Pi will start in in Wireless router mode giving out Wi-Fi network name as IOTKit-Pi3
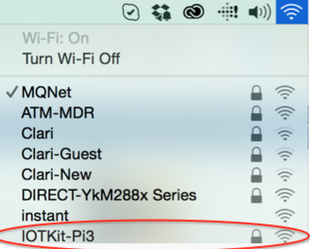
- Connect your laptop to IOTKit-Pi3 Wi-Fi network name using password atomiton
- Launch a web browser and type http://1.1.1.1:8080/fid-kitsetupui/index.html
- Configure your personal Wi-Fi Network. Note that you can configure multiple Wi-Fi Networks.
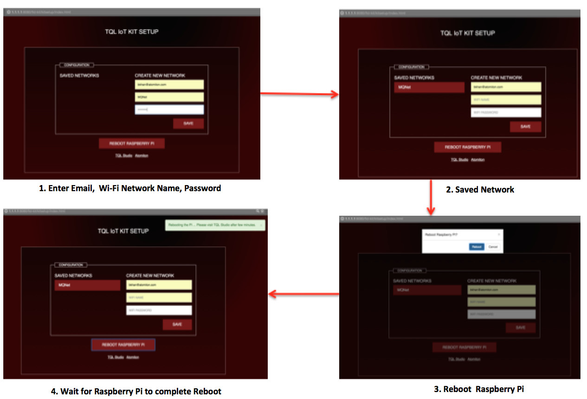
- After Raspberry Pi rebooted, connect your laptop back to your personal Wi-Fi network.
- Login to TQLStudio portal using your TQLStudio credentials.
- Click on any of your project and go to Thing Spaces to view the IP address assigned to IoTKit Raspberry Pi
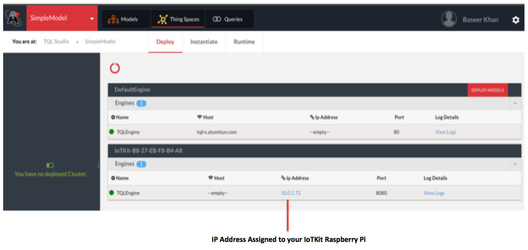
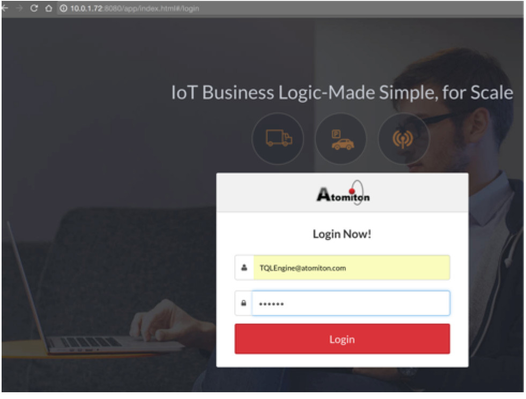
- Launch TQLEngine User Interface by clicking on the IP Address link
- Login to TQLEngine UI default credentials [Username: TQLEngine@atomiton Passwrod: tql123]
- You will find two default projects loaded - IoTKitThings and IoTKitSetup
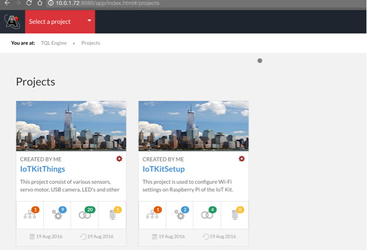
- Refer to Working with IoTKit Things below.
Working with IoTKit Things
Working with Sensors
Detect Serial Port
<Query>
<Find format="version,Known">
<SerialPortModel>
<ID ne=""/>
</SerialPortModel>
</Find>
<if condition="$Response.Message.Value/Find/Status eq 'Success'">
<then>
<DeleteAll>
<SerialPortModel>
<ID ne=""/>
</SerialPortModel>
</DeleteAll>
</then>
</if>
<Create>
<SerialPortModel>
<PortName>
$Null()
</PortName>
<Baudrate>
9600
</Baudrate>
<DefaultPort>
/dev/cu.usbmodem1411
</DefaultPort>
</SerialPortModel>
</Create>
</Query>
Get Serial Port
<Query>
<Find format="version, known">
<SerialPortModel>
<ID ne=""/>
</SerialPortModel>
</Find>
</Query>
Get Serial Port Response
PortName attributes "Known" value contains the Serial Port on which the Arduino is connected to the Raspberry Pi. The value here is: /dev/ttyACM0
<Find Status="Success" Format="version, known">
<Result>
<SerialPortModel>
<ID>K264G7FLAAAH6AABAF46QU4Z</ID>
<PortName Value="" Known="/dev/ttyACM0
" Version="1"/>
<Baudrate Value="9600" Known="9600" Version="1"/>
<DefaultPort Value="/dev/cu.usbmodem1411" Known="/dev/cu.usbmodem1411" Version="1"/>
</SerialPortModel>
</Result>
</Find>
Arduino Sketch
The Arduino Sketch uses two other libraries,
- OneWire
- Dallas Temperature
this libraries can be imported in the Arduino IDE, below are the steps to install the libraries
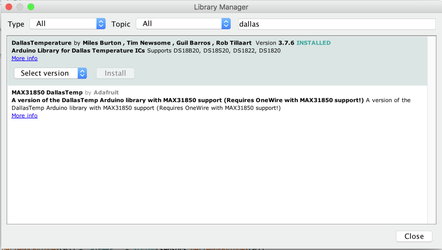
- In the toolbar menu select sketch, then Include Library→ Manage Libraries option.
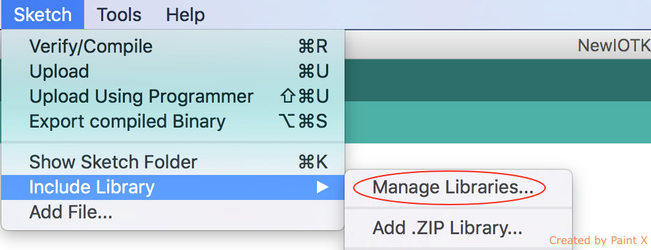
- Search for the Dallas Temperature library and Install it, similarly search for one wire library and install it.
#include <math.h>
#include <Servo.h>
#include <OneWire.h>
#include <DallasTemperature.h>
#define ONE_WIRE_BUS 12 /*-(Connect to Pin 12 )-*/
/*-----( Declare objects )-----*/
/* Set up a oneWire instance to communicate with any OneWire device*/
OneWire ourWire(ONE_WIRE_BUS);
/* Tell Dallas Temperature Library to use oneWire Library */
DallasTemperature sensors(&ourWire);
//Create servo object
Servo myservo;
int sensorPinL = A4; // select the input pin for the potentiometer
String inData;
int redPinOne = 1;
int greenPinOne = 2;
int bluePinOne = 3;
int redPinTwo = 5;
int greenPinTwo = 6;
int bluePinTwo = 7;
int redPinThree = 9;
int greenPinThree = 10;
int bluePinThree = 11;
String getTemperature() {
sensors.requestTemperatures();
String tempStr = "TEMPC:" + String(sensors.getTempCByIndex(0)) + "#TEMPF:" + String(sensors.getTempFByIndex(0));
//String tempStr = "TEMPC:" + String((int)sensors.getTempCByIndex(0)) + "#TEMPF:" + String((int)sensors.getTempFByIndex(0));
return tempStr;
}
//KY015 DHT11 Temperature and humidity sensor
int DHpin = 8;
byte dat [5];
byte read_data () {
byte data = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i ++) {
if (digitalRead (DHpin) == LOW) {
while (digitalRead (DHpin) == LOW); // wait for 50us
delayMicroseconds (30); // determine the duration of the high level to determine the data is '0 'or '1'
if (digitalRead (DHpin) == HIGH)
data |= (1 << (7 - i)); // high front and low in the post
while (digitalRead (DHpin) == HIGH); // data '1 ', wait for the next one receiver
}
}
return data;
}
void start_test () {
digitalWrite (DHpin, LOW); // bus down, send start signal
delay (30); // delay greater than 18ms, so DHT11 start signal can be detected
digitalWrite (DHpin, HIGH);
delayMicroseconds (40); // Wait for DHT11 response
pinMode (DHpin, INPUT);
while (digitalRead (DHpin) == HIGH);
delayMicroseconds (80); // DHT11 response, pulled the bus 80us
if (digitalRead (DHpin) == LOW);
delayMicroseconds (80); // DHT11 80us after the bus pulled to start sending data
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++) // receive temperature and humidity data, the parity bit is not considered
dat[i] = read_data ();
pinMode (DHpin, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite (DHpin, HIGH); // send data once after releasing the bus, wait for the host to open the next Start signal
}
String getHumidity () {
start_test ();
String hum = "";
hum = "HUMPCT:" + String(dat [0], DEC) + "." + String(dat [1], DEC);
return hum;
}
int ledPin = 13; // select the pin for the LED
String getLight() {
String amb = "";
int sensorValue = 0; // variable to store the value coming from the sensor
sensorValue = analogRead(sensorPinL);
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
delay(sensorValue);
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
delay(sensorValue);
amb = "AMB:" + String(sensorValue, DEC);
return amb;
}
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.setTimeout(500);
pinMode(redPinOne, OUTPUT);
pinMode(greenPinOne, OUTPUT);
pinMode(bluePinOne, OUTPUT);
pinMode(redPinTwo, OUTPUT);
pinMode(greenPinTwo, OUTPUT);
pinMode(bluePinTwo, OUTPUT);
pinMode(redPinThree, OUTPUT);
pinMode(greenPinThree, OUTPUT);
pinMode(bluePinThree, OUTPUT);
pinMode (DHpin, OUTPUT);
pinMode (ledPin, OUTPUT);
myservo.attach(4);
sensors.begin(); // For Temperature Sensor Begin Dallas Library
}
void RGB_control(String temp, int light)
{
int redval = temp.charAt(0) - '0';
int greenval = temp.charAt(1) - '0';
int blueval = temp.charAt(2) - '0' ;
switch (light)
{
case 1:
digitalWrite(redPinOne, redval);
digitalWrite(greenPinOne, greenval);
digitalWrite(bluePinOne, blueval);
break;
case 2:
digitalWrite(redPinTwo, redval);
digitalWrite(greenPinTwo, greenval);
digitalWrite(bluePinTwo, blueval);
break;
case 3:
digitalWrite(redPinThree, redval);
digitalWrite(greenPinThree, greenval);
digitalWrite(bluePinThree, blueval);
break;
}
}
void loop() {
inData = "";
if (Serial.available() > 0)
{
int h = Serial.available();
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++) {
inData += (char)Serial.read();
}
if (inData.indexOf("RGB") >= 0)
{
RGB_control(inData.substring(6, 9),(int)(inData.charAt(4)-'0'));
}
else
{
myservo.write(inData.toInt());
}
}
Serial.println(getTemperature() + "#" + getHumidity() + "#" + getLight());
delay(1000);
}